GHG emissions inventory provides the basis for emission reduction
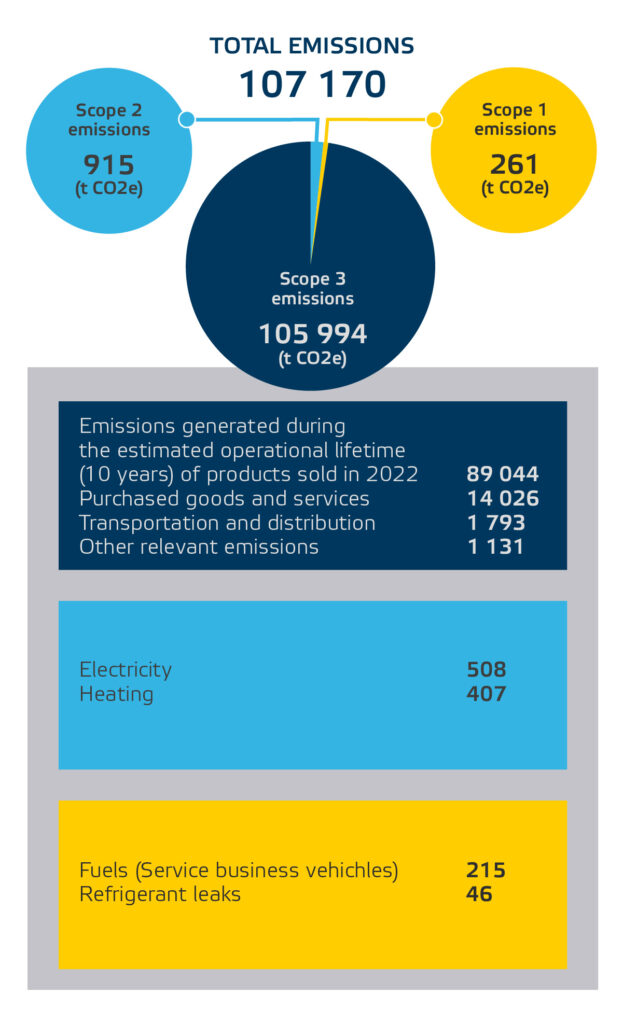
Teleste expanded its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions inventory in 2023 to include Scope 3 emissions. Our emission inventory demonstrates that Teleste’s carbon footprint is mainly generated in our value chain.
The most significant source of Teleste’s GHG emissions arises from the use of our products during their lifetime. The magnitude these emissions is influenced by the products’ energy consumption, and, most importantly, the environmental friendliness of the energy used. Another influencing factor is the duration of product use. We used an estimated 10-year lifespan as a basis for our calculations.
Long-term development of the energy efficiency of products
Improving the energy efficiency of our products has been one of the priorities of our product development activities for several decades. In all of our business lines, our products are designed for maximum efficiency without compromising on performance. Our customers benefit from this by having not only highly performing equipment but also decreasing energy consumption and lower electricity costs.
“As a technology company, we have a significant opportunity and responsibility to be at the leading edge of sustainable development by creating new innovations and adopting green technologies and eco-friendly materials.”
Pasi Järvenpää, Senior Vice President, Research and Development
For example, our Intelligent Networks technology has enabled us to launch network devices that optimise their power consumption according to the network’s actual capacity usage. Broadband networks are large in scale, which means that even minor improvements in the efficiency of equipment can reduce total energy consumption and, consequently, the carbon footprint. Many of our intelligent devices and software products can also be controlled and maintained remotely, which reduces on-site maintenance activities and cuts down our customers’ fuel costs and emissions.
Reliability is at the core of sustainable solutions
In our product design, we take account of the full life cycle environmental impacts of our products. This is reflected in a strong focus on product durability and serviceability. Most of our devices have a considerably long technical life cycle spanning up to decades. Instead of having to be replaced every few years, they serve our customers far into the future. We use a number of design tools to ensure the reliability of our products. Examples of these tools include Design Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Design FMEA), which aims to prevent quality problems by revealing potential technical defects and enabling the necessary adjustments and corrections in the design stage.
Our products are designed to be recyclable at the end of their technical life cycle. For example, most of our network devices feature aluminium housing that can be disassembled into a single-material part for reuse. We also actively avoid the use of materials that are non-recyclable or otherwise involve adverse environmental impacts or concerns.


